Carrying gear shouldn’t slow you down. Research shows ergonomic bags can reduce shoulder strain by up to 50%, lower muscle fatigue by 60%, and improve posture, helping teams perform better. These designs redistribute weight to the hips, reducing back and shoulder stress while improving balance and comfort.
Key takeaways:
- Weight distribution matters: Hip belts and chest straps shift load from shoulders to hips, cutting strain.
- Better posture: Ergonomic bags reduce forward trunk lean by nearly half compared to standard bags.
- Energy efficiency: Properly designed bags conserve energy by minimizing unnecessary muscle effort.
- Custom features: Adjustable straps, lumbar support, and side pockets improve fit, balance, and accessibility.
Whether for sports or business, ergonomic bags help teams move efficiently, reduce injury risks, and stay focused. Investing in well-designed bags means arriving ready to perform, not exhausted.
How to choose a comfortable backpack: 3 ergonomic tips to protect your posture and your health
Ergonomic Bag Design Principles
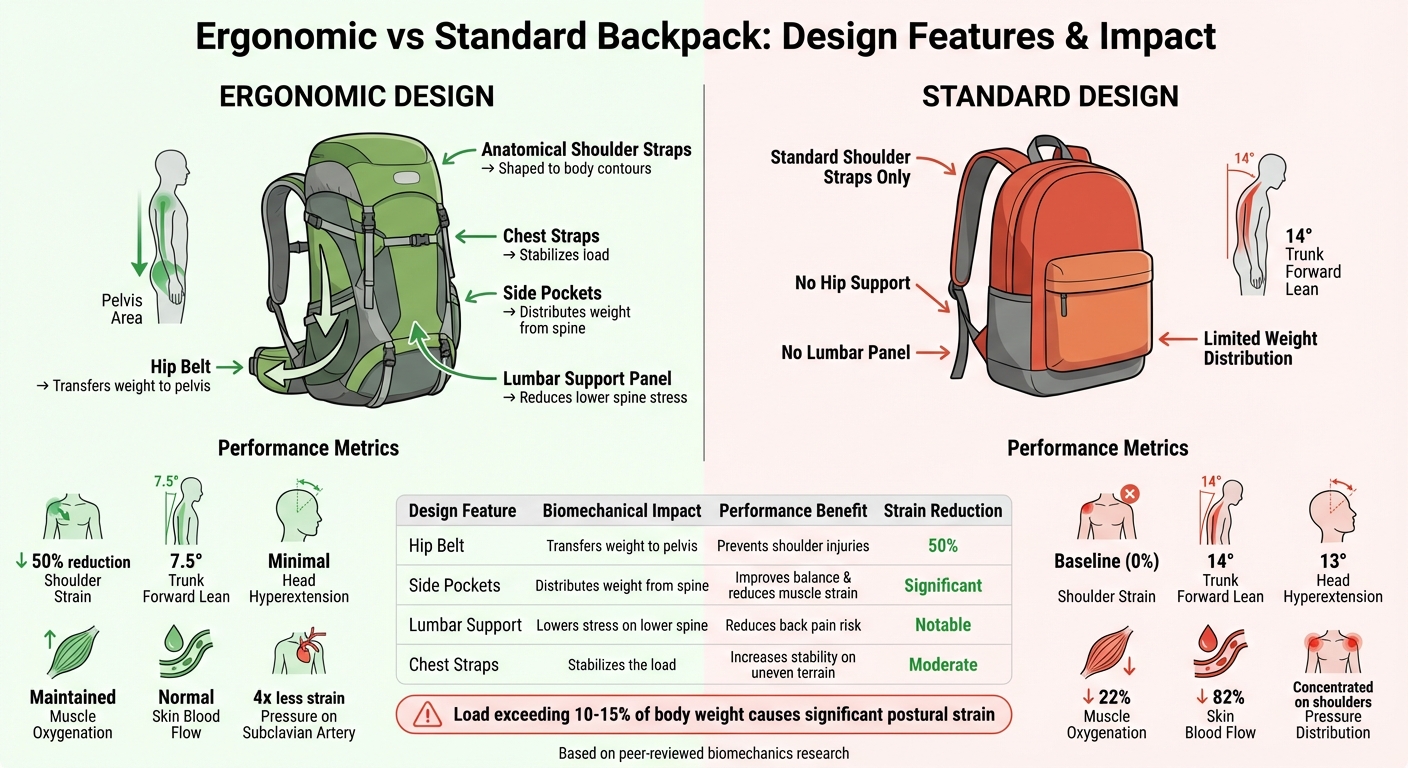
Ergonomic vs Standard Backpack Design Features and Benefits Comparison
Ergonomic bag design revolves around three core ideas: transferring the load from vulnerable areas, keeping the weight close to the body, and evenly distributing it. These principles address the physical challenges of carrying gear. Let’s dive into how proper weight distribution supports these goals.
The most crucial aspect is shifting weight from the shoulders to the pelvis. Studies show that the hip region can handle much more pressure than the shoulders, making hip belts a key feature. In fact, ergonomic backpacks can reduce shoulder strain by 50% compared to traditional two-strap bags. This adjustment prevents injuries like "rucksack palsy", a shoulder condition often seen in athletes carrying heavy loads without proper support.
"In order to minimize discomfort, users should be encouraged to shift load from the shoulders to the hip region wherever possible, at the same time likely decreasing the risk of low back pain or injury." – PLOS One
Symmetrical loading is just as important. Designs with side pockets or front-back compartments help maintain an upright posture more effectively than traditional backpacks. For example, carrying a conventional bag with 25% of body weight causes the trunk to lean forward by around 14°, with the head hyperextending by 13°. In contrast, bilateral designs reduce this forward lean to about 7.5°, keeping the body closer to its natural posture.
Weight Distribution and Load Balancing
Spreading the load across multiple contact points is key. Features like hip belts, chest straps, and lumbar support panels help distribute weight across the torso, instead of concentrating it on the shoulders and spine. For instance, when a 10kg backpack rests solely on the shoulders, it can reduce shoulder muscle oxygenation by 22% and skin blood flow by 82%. This leads to fatigue and discomfort, especially during extended activity.
Positioning the load high and close to the back is critical. Research from Applied Ergonomics found that keeping the load near the body’s center of gravity minimizes energy use during movement. Side pockets also play a role by redistributing heavier items away from the spine, which improves balance and reduces muscle strain. A study at King Saud University demonstrated this with a backpack design that used upper and lower straps to attach side pockets, significantly reducing muscle strain in the trapezius and erector spinae.
Lumbar support panels add another layer of comfort and protection, reducing stress on the lower spine and lowering the risk of back pain. For teams traveling with gear or heading to tournaments, this feature can mean the difference between arriving ready to perform or exhausted.
| Design Feature | Biomechanical Impact | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hip Belt | Transfers weight to the pelvis | Reduces shoulder strain and prevents injuries |
| Side Pockets | Distributes weight from the spine | Improves balance and reduces muscle strain |
| Lumbar Support | Lowers stress on the lower spine | Reduces risk of back pain |
| Chest Straps | Stabilizes the load | Increases stability on uneven terrain |
Accessibility and Functional Features
Convenience features like easy-access compartments and adjustable straps improve how users interact with their gear. Multi-point strap systems ensure a fit for a wide range of body sizes, accommodating users from the 5th to the 95th percentile.
Quick-access side or front pockets allow athletes to grab essentials without removing the bag, saving time during practices or games. These compartments also help distribute weight more evenly, taking pressure off the back.
Shorter, stiffer shoulder straps improve stability by limiting the bag’s movement during dynamic activities like running or navigating uneven surfaces. This reduces the need for constant adjustments and helps athletes stay focused. Research shows that strap design accounts for over 85% of variations in user-reported discomfort, making it one of the most important aspects of overall comfort.
Body Measurement Adaptation
Designing bags to fit individual body measurements ensures proper weight distribution and reduces strain. Ergonomic designs must account for anthropometric differences – variations in body size and shape. Adjusting for factors like shoulder height, shoulder width, and abdominal circumference ensures the bag fits comfortably and avoids concentrating force on specific areas.
For younger users, this is especially critical. Carrying loads exceeding 10-15% of body weight can cause significant forward head tilt and postural strain. Adjustable features that grow with the athlete are essential for youth teams. Adults face different challenges – traditional backpacks carrying 25% of body weight cause pronounced forward lean, but designs tailored to body measurements can cut this lean in half.
Anatomical straps shaped to match the contours of the body can reduce strain on the subclavian artery by 4 times and lower skin stress by 50% compared to standard straps. This precision prevents blood flow issues, which can start at pressure levels as low as 5.6 kPa and become severe above 16 kPa. For teams investing in custom bags, these measurements provide clear benchmarks for achieving the best possible design.
Research Methods Used to Test Ergonomic Bags
This research highlights how specific design features improve ergonomic performance, building on earlier discussions about weight distribution and accessibility.
Testing ergonomic bags involves tools that measure both physical strain and user experience. One key method is surface EMG (electromyography), which tracks muscle activity. This technology measures electrical signals from muscles like the trapezius, erector spinae, multifidus, and external abdominal obliques while participants carry loaded bags, either walking or standing. Researchers normalize the data to a percentage of maximum voluntary contraction (%MVC) for accurate comparisons.
Motion capture systems add another layer of analysis. Systems like XSENS Awinda and Polhemus LIBERTY track joint angles and range of motion in the spine and lower body. For example, in January 2025, researchers at Bahcesehir University‘s Biomechanics Lab used the XSENS Awinda system alongside Trigno Wireless EMG to study 20 adults carrying bags weighing 12% of their body weight. They found that carrying a backpack restricted spinal joint movement and increased hip rotation, especially when walking on flat surfaces and 5° inclines.
Pressure mapping technology pinpoints areas where force concentrates on the body. Tekscan sensors placed under shoulder straps and hip belts measure peak and average pressure in kilopascals (kPa). Research shows blood flow restriction begins at 5.6 kPa, with severe effects at 16 kPa. Additionally, force sensors measure strap tension in Newtons, which can explain 85% or more of the variation in reported discomfort. These methods provide detailed insights into how loads affect muscles and pressure points under various conditions.
Muscle Activity and Load Analysis
EMG data offers real-time insights into how specific muscles respond to carrying loads. For instance, in April 2015, researchers led by Gerwyn Hughes at the University of Hertfordshire studied 12 female students walking on a treadmill at 1.1 m/s. They compared five carrying styles – including one-strap and two-strap configurations – with loads equal to 10% of body weight. The study revealed that two-strap rucksacks reduced trapezius muscle activity significantly compared to asymmetrical carrying methods. This type of analysis helps pinpoint which muscles bear the most strain, guiding adjustments in bag design.
In another study from May 2020, researchers at King Saud University used data from 280 students to develop an ergonomic backpack. Their findings showed lower EMG responses in key muscle groups compared to standard commercial bags. The prototype featured side pockets to better distribute weight, reducing strain on the erector spinae at 15% and 20% body weight loads. This demonstrates how specific design features can alleviate strain without merely shifting it elsewhere.
"The developed backpack design confirmed the efficiency of its bases by distributing the carried weight among the trunk through side pockets… It helped the body to distribute the carried weight and avoid concentrating pressure on specific areas." – Mohamed Z. Ramadan, Industrial Engineering Department, King Saud University
Building on these findings, further tests compare the performance of ergonomic designs against standard bags under controlled conditions.
Ergonomic vs. Standard Bags Comparison
To ensure consistent results, researchers use controlled conditions when comparing ergonomic and standard bags. A common setup involves treadmill walking at a set speed – typically 1.1 m/s (about 4 km/h) – on flat surfaces or inclines ranging from 5° to 8°. Some labs even use instrumented dummies equipped with skin-analog foam and load cells to provide objective, repeatable measurements without human variability.
For example, in June 2017, a study published in PLOS ONE validated an instrumented dummy by comparing its data to results from 10 male participants. The dummy tested 12 configurations of a Deuter ACT Lite backpack, measuring average pressure and strap forces. The researchers found the dummy could explain 79% or more of the variance in human discomfort.
These comparisons combine biomechanical data with user feedback. Participants rate comfort on standardized scales, such as 0 to 7 or 0 to 10, allowing researchers to correlate physical measurements with perceived discomfort. When King Saud University researchers tested their ergonomic prototype against commercial bags, they found that comfort ratings aligned closely with EMG readings, validating both the design improvements and the testing approach. This dual method ensures that ergonomic bags perform well in both lab settings and everyday use.
| Measurement Method | Tools Used | Primary Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle Activity | Surface EMG (Biometrics, Trigno Wireless) | %MVC, RMS Voltage, Muscle Fatigue |
| Mechanical Load | Tekscan Sensors, Load Cells | Peak/Average Pressure (kPa), Strap Tension (N) |
| Kinematics | Motion Capture (XSENS, Polhemus LIBERTY) | Joint ROM, Trunk Lean, Spinal Flexibility |
| Subjective Assessment | Comfort Rating Scales, Questionnaires | Discomfort Score (0-10) |
These findings emphasize the importance of thoughtful design in creating ergonomic bags that balance functionality and comfort for users.
sbb-itb-1e6451b
Performance Benefits for Teams
Research highlights how ergonomic design and optimal weight distribution go beyond mere comfort, delivering measurable performance advantages for teams. These benefits influence how team members move, maintain posture, and perform during activities that involve carrying gear.
Reduced Muscle Strain and Better Posture
Ergonomic bags are designed to significantly reduce physical strain by strategically distributing weight. Studies show that these designs can cut shoulder load by 50% compared to traditional backpacks. This reduction occurs because ergonomic bags shift the weight from the shoulders and spine – areas prone to strain – to the pelvic region, which is better equipped for handling heavy loads.
Another key benefit is improved posture. Traditional backpacks often lead to a 14° forward trunk lean and a 13° head hyperextension, which can strain the back and neck. In contrast, ergonomic designs with bilateral support limit trunk flexion to about 7.5° and minimize changes in head angle, reducing discomfort and the risk of back pain.
"The more upright posture supported by the BTP may help reduce characteristics of poor posture and, ideally, help to reduce low back pain while carrying loads." – Gait & Posture, Volume 45
Ergonomic features also maintain muscle oxygenation and reduce pain during extended use. Wider, padded shoulder straps and hip belts prevent compression, ensuring healthy circulation. This combination of better posture and reduced strain allows for smoother, more efficient movement.
Improved Efficiency in Team Activities
The advantages of ergonomic design extend to overall team performance by enhancing functional efficiency. Proper weight distribution directly improves mobility, particularly for sports teams and work crews. When loads are imbalanced, individuals often compensate with smaller, quicker steps, which increases energy use and reduces walking efficiency. Ergonomic bags, by maintaining the body’s natural center of mass, enable normal gait patterns even under heavy loads.
Energy efficiency is another critical factor. Carrying a load equal to 30% of body mass can demand up to 41% of VO2max, nearing the limit for sustainable activity. Features like high and tight load placement, combined with hip belt support, reduce the muscle effort required to stabilize posture, conserving energy for primary tasks.
For teams navigating uneven terrain or enduring long events, hip belts offer additional benefits by enhancing lateral stability and balance. The pelvic region is far better at handling pressure than the shoulders, making load-shifting features essential for reducing fatigue during extended activities like tournaments, fieldwork, or multi-day operations. Packing heavier items closer to the back and higher on the frame further optimizes balance and minimizes muscle strain.
Applications for Team Sports and Business Use
Research-backed ergonomic principles are shaping practical bag designs that help teams in sports and business reduce physical strain while boosting efficiency. These designs focus on improving load distribution and making it easier to transport essential gear.
Features for Team Gear Transport
Sports bags designed for teams often include ergonomic features aimed at making gear transport more efficient and less taxing on the body. For instance, hip belts shift weight from the shoulders to the pelvis, which is better equipped to handle pressure. This adjustment helps alleviate the strain typically associated with carrying heavy loads.
Adjustable straps and side pockets are other key features. These ensure the load stays close to the body, improving balance and reducing muscle fatigue. For teams sharing equipment bags, adjustable strap systems allow users of different body sizes to carry the load comfortably. Side pockets help evenly distribute weight across the trunk, preventing undue stress on the spine and reducing the risk of poor posture.
Additionally, specialized compartments can be incorporated to meet the organizational needs of teams, all while maintaining ergonomic advantages.
Custom Bag Solutions with JUNYUAN BAGS
JUNYUAN BAGS takes these ergonomic benefits a step further by offering custom-designed solutions tailored to the specific needs of teams. Their design process allows teams to specify features like adjustable dual-strap systems and load-balancing side compartments, all based on anthropometric data such as shoulder breadth and sitting shoulder height. These adjustments help reduce musculoskeletal strain.
Customization options include materials, logos, sizes, and internal layouts. Teams can choose waterproof synthetics for outdoor sports or premium materials for business settings. Internal dividers and specialized compartments are also available, offering quick access to gear during events or business activities. For teams carrying heavy equipment, features like fence hooks and padded compartments for electronics can be added. These tailored designs maintain ergonomic benefits – such as reducing shoulder strain by up to 50% – while meeting each team’s unique needs.
Conclusion
Research highlights that ergonomic bag designs significantly improve team performance and overall well-being. By redistributing the load from the shoulders and spine to the pelvic region, these designs can reduce shoulder strain by up to 50%. They also address over 85% of discomfort caused by static peak pressure and strap force.
Teams using these bags benefit from better posture, reduced muscle fatigue, and smoother movement. These ergonomic features help maintain natural body alignment and balance, making tasks less physically taxing.
For businesses and teams, investing in ergonomic bags is a practical choice. Features like hip belts, adjustable dual straps, and balanced compartments lower the risk of musculoskeletal injuries, improve efficiency, and allow workers to focus on their tasks without being hindered by discomfort or fatigue.
"A newly designed EBP [ergonomic backpack] was effective at transferring a significantly large portion of the shoulder and spine loads to the pelvic region." – PubMed, National Library of Medicine
Organizations can collaborate with manufacturers such as JUNYUAN BAGS to develop custom solutions tailored to their needs. By combining proven ergonomic principles with tailored designs, companies can provide their teams with bags that safeguard their health while enhancing productivity.
FAQs
How can ergonomic bags enhance team performance?
Ergonomic bags can enhance team performance by prioritizing comfort and reducing physical strain. Features such as even weight distribution, adjustable straps, and supportive belts are designed to ease muscle fatigue and joint stress. This allows team members to remain focused and perform at their best.
During group activities or tasks that demand extended physical effort, these bags support better posture and smoother movement. By minimizing discomfort and lowering the risk of injury, ergonomic bags help teams work more efficiently and sustain high productivity levels over longer periods.
What should I look for in an ergonomic bag to improve comfort and performance?
When picking an ergonomic bag, pay attention to features that improve comfort and ease the strain on your body. Key elements to look for include padded shoulder straps, an adjustable hip belt, and a supportive back panel. These features help distribute weight evenly, taking pressure off your shoulders and spine.
Other helpful details to consider are adjustable straps, lightweight materials, and contoured designs that fit naturally to your body. A good hip belt is especially important – it shifts the weight to your hips, which can handle it more effectively, reducing both fatigue and discomfort. These thoughtful design choices can significantly improve how the bag feels and performs during use.
Can ergonomic bags help prevent long-term injuries?
Ergonomic bags are crafted to help reduce strain on your body by evenly spreading out the weight you carry and lessening biomechanical stress. Studies reveal that carrying loads the wrong way can lead to discomfort and, over time, may even cause long-term injuries. Features like padded straps, adjustable settings, and balanced weight distribution play a big role in lowering these risks.
These designs focus on comfort and functionality, promoting better posture and easing the burden on your muscles and joints. Whether you’re using them daily or for more physically demanding activities, they’re a smart choice to keep you moving comfortably.




 Mobile/What's App/Wechat
Mobile/What's App/Wechat E-Mail
E-Mail ADD
ADD




