Water recycling in bag production is transforming how manufacturers use and reuse water during fabric and material processing. This process reduces water consumption and pollution while cutting costs. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Water Use in Bag Manufacturing: Processes like dyeing, washing, and finishing fabrics require significant amounts of water. For instance, dyeing alone uses 7–8 times the fabric’s weight in water.
- Recycling Process: Wastewater is collected, treated through filtration and purification (e.g., reverse osmosis), and reused in production. Advanced systems can recover up to 95% of water.
- Benefits: Saves water, reduces pollutants, lowers operational costs, and ensures production continues during water shortages.
- Challenges: Treating wastewater with complex contaminants can be costly, but modern technologies like ultrafiltration and automated monitoring systems are improving efficiency.
SACOS DE JUNYUAN exemplifies this approach by using recycled materials like RPET and water reuse systems, balancing production needs with resource conservation.
Water Usage in Standard Bag Manufacturing
High Water Consumption Processes
Making sports and travel bags involves processes that consume a lot of water. Key stages like pretreatment, dyeing, printing, and finishing fabrics are especially demanding. To put it into perspective, processing just 1 kilogram of fabric can use up to 200 liters (53 gallons) of water.
Dyeing takes a significant toll because it requires dissolving dyes in water, followed by multiple washes to remove excess pigments. On average, this process uses 7–8 times the fabric’s weight in water. For bags made from recycled plastics, the cleaning and washing of contaminated plastics before processing also generate large amounts of wastewater. A single plastic washing line can consume around 25 cubic meters of water per hour – that’s approximately 6,600 gallons every hour.
The type of material being processed plays a big role in water usage. For instance, cotton requires 100–125 liters of water per kilogram during textile processing, while synthetic fibers like polyester use anywhere from 70 to 136 liters per kilogram during processing and dyeing. Even routine tasks, such as cleaning equipment and floors, add to the overall water demand. These high water needs highlight the importance of incorporating recycling measures.
Challenges of Conventional Water Use
The heavy water demands of traditional bag manufacturing put significant pressure on water resources. For every liter of untreated wastewater released, it can contaminate 5 to 8 liters of local groundwater. Shockingly, about 40% of industrial wastewater is discharged into the environment without proper treatment.
Many manufacturers face inefficiencies due to outdated or insufficient systems for monitoring water flow. This often leads to unnecessary waste, especially during rinsing and washing steps. Treating the resulting wastewater is another hurdle – it often contains complex contaminants that are both difficult and costly to remove. In some areas, the expense of treating wastewater can even surpass the cost of buying fresh water. If these practices persist, experts predict a 40% gap between global water supply and demand by 2030. Tackling these inefficiencies is essential to make bag production more sustainable.
Dyed without waste – developing a process to save water in the textile industry
Main Steps in the Water Recycling Process
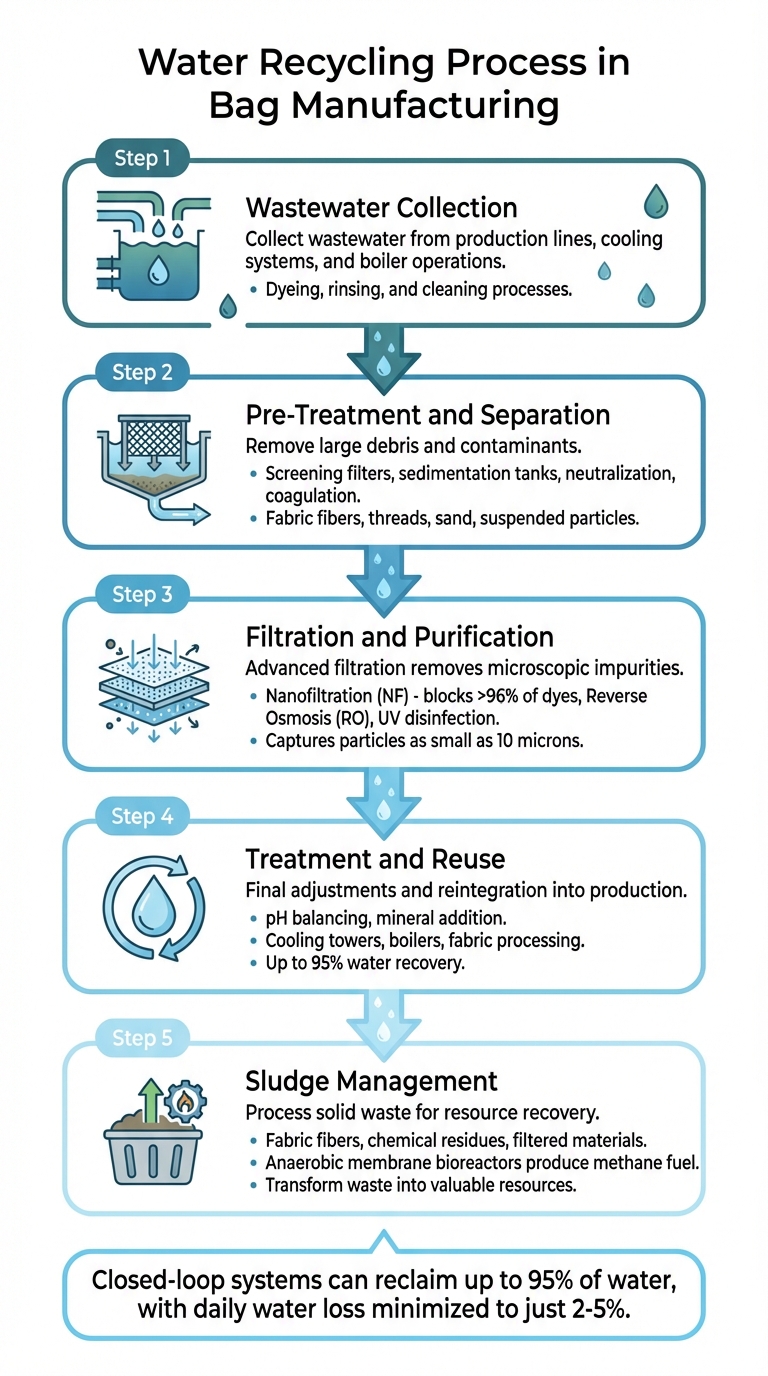
5-Step Water Recycling Process in Bag Manufacturing
Step 1: Wastewater Collection
The journey of recycling water begins with collecting wastewater from various points within the manufacturing facility. This includes water from production lines, cooling systems, and boiler operations. In the case of bag manufacturing, wastewater from processes like dyeing, rinsing, and cleaning is gathered through specialized collection systems. The captured water is then directed into holding tanks or sent straight to onsite treatment facilities. As the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency explains, "Water reuse is the practice of reclaiming water from a variety of sources, treating it, and reusing it for beneficial purposes". Once collected, this water moves to pre-treatment, where larger contaminants are removed.
Step 2: Pre-Treatment and Separation
After collection, the wastewater undergoes an initial cleaning phase to eliminate large debris. Screening filters remove materials like fabric fibers and threads, while sedimentation tanks allow heavier particles, such as sand, to settle at the bottom. For processes involving dyed fabrics, this step also includes neutralization and coagulation – chemical treatments that balance pH levels and group suspended particles for easier removal. This stage is critical for protecting the more delicate filtration systems used later. Once pre-treated, the water is ready for advanced filtration to achieve finer purification.
Step 3: Filtration and Purification
The pre-treated water then moves through advanced filtration systems designed to remove even the smallest impurities. Technologies like nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes are employed to filter out fine particles, chemical residues, and dissolved dyes. Nanofiltration, which can block over 96% of certain dyes, acts as a preliminary safeguard before reverse osmosis tackles smaller organic molecules and salts. Additional disinfection steps, such as ultraviolet light or chlorine treatment, and automated filters capable of capturing particles as small as 10 microns, ensure the water meets stringent reuse standards.
Step 4: Treatment and Reuse
Once purified, the water undergoes final adjustments to prepare it for reuse. pH levels are fine-tuned to prevent corrosion in pipes, and minerals may be added to meet specific manufacturing needs. The recycled water is then reintegrated into non-drinking applications like cooling towers, boilers, and certain fabric processing stages. Many bag manufacturing facilities adopt this approach, using recycled water in cooling systems and fabric production to significantly cut down on water consumption. As the EPA highlights, "By using recycled water, the refinery’s operations remain unaffected by drought restrictions, and demonstrate that recycled water is a practical solution for a reliable, drought-resistant water supply".
Step 5: Sludge Management
The purification process generates solid waste, known as sludge, which contains fabric fibers, chemical residues, and other filtered materials. Automated systems are used to separate these solids from the water, reducing the need for manual handling. Instead of discarding the sludge in landfills, some advanced facilities process it to extract usable resources. For instance, anaerobic membrane bioreactors break down organic matter with the help of microbes, producing methane gas that can be used as fuel. In some cases, nutrients are even recovered from the sludge, transforming waste into valuable resources.
sbb-itb-1e6451b
Technologies Used in Water Recycling for Bag Production
Closed-Loop Recycling Systems
Modern bag manufacturing facilities are increasingly turning to closed-loop systems to treat wastewater as a reusable resource. These systems recycle water continuously within the facility, significantly cutting down the need for fresh water.
"Industrial water systems are moving from linear to circular design" – Jason Bowman, Director of Industrial Wastewater and Biogas at Fluence Corp
These advanced recycling setups can reclaim up to 95% of water. The process is designed so that purified water flows directly back into production areas like cooling towers, boilers, and fabric processing units, maintaining a seamless closed-loop cycle. This approach also supports more efficient filtration and treatment methods.
Filtration and Treatment Technologies
Filtration and treatment systems play a critical role in ensuring water purity within closed-loop systems. These systems rely on multi-stage filtration to remove contaminants, starting with larger particles and working down to microscopic impurities. High-speed centrifuges, spinning at up to 4,100 rpm, eliminate suspended particles. From there, water passes through flotation, band, sand, and bag filters.
For finer purification, membrane-based technologies take over. Ultrafiltration and microfiltration remove pathogens and smaller particles, while reverse osmosis eliminates up to 99% of dissolved salts and ions. In cases where ultra-pure water is needed, methods like electrodeionization or ion exchange resins refine water to nanogram-per-liter purity levels. Additionally, chemical treatments such as flocculation help clump fine particles together, making them easier to extract.
Automated Monitoring Systems
Automation has become a cornerstone of maintaining recycled water quality, ensuring it consistently meets production standards. Submeters and pressure sensors monitor water flow at various production stages, quickly identifying leaks or equipment issues when unexpected pressure drops occur. Centralized systems provide real-time alerts and detailed reports.
"You can’t manage what you don’t measure" – EPA’s Lean & Water Toolkit
Automated control units also handle precise chemical dosing during water treatment, using just the right amount of flocculants and other chemicals. These systems maintain pH levels within the optimal range of 6.5 to 9.5 for physical treatment processes. They also supply detailed hourly and daily data, helping facilities track and improve efficiency over time.
Water Conservation at SACOS DE JUNYUAN
Eco-Friendly Practices in Bag Production
JUNYUAN BAGS has earned international certifications like BSCI e ISO, reflecting its commitment to responsible manufacturing and environmental care. One standout initiative is the integration of RPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate) into its bag production. By converting recycled plastic waste into tough, reusable fabrics, the company not only minimizes plastic waste but also promotes a closed-loop manufacturing process that prioritizes sustainability.
Another notable effort is JUNYUAN BAGS’ water recycling system, which ensures uninterrupted production even during local water restrictions. This system goes beyond operational benefits – it helps conserve community water supplies, secures drinking water sources for nearby residents , prevents nitrogen pollution in local waterways, and mitigates land subsidence caused by excessive groundwater extraction. These initiatives demonstrate how the company balances resource conservation with delivering practical benefits to its customers.
Benefits for Customers and the Environment
JUNYUAN BAGS’ focus on sustainability doesn’t stop at environmental stewardship – it also benefits its customers. By combining water recycling systems with eco-conscious materials like RPET, the company produces durable and customizable products, including backpacks and other bags, that meet high environmental standards.
The emphasis on water efficiency also helps lower energy use, chemical consumption, and compliance costs. These savings enable JUNYUAN BAGS to offer competitively priced products without compromising its commitment to environmentally responsible practices – an approach validated by its BSCI and ISO certifications.
Conclusão
Water recycling has become a game-changer for sustainable bag manufacturing, offering both environmental and financial advantages. With modern closed-loop systems, daily water loss can be minimized to just 2–5%. By treating and reusing wastewater on-site, manufacturers not only conserve precious freshwater resources but also reduce pollution in local waterways and ensure smooth operations, even during droughts.
The economic benefits are equally compelling. Recycling water internally helps companies avoid hefty discharge fees, which can soar to as much as $126 million for improper wastewater disposal.
"By reusing water within their own facilities, businesses can significantly reduce both operational costs and environmental impact, all while building resilience against supply risks and regulatory pressures."
– Target Recycling Services Inc.
These combined benefits highlight why industry leaders are prioritizing such systems.
JUNYUAN BAGS exemplifies this approach, integrating water recycling into its operations to meet environmental goals while supporting sustainable production. Their system not only ensures uninterrupted manufacturing during local water restrictions but also conserves water resources for over 83,000 nearby residents. Backed by BSCI and ISO certifications and the use of RPET materials, the company strikes a balance between eco-conscious practices and delivering durable, customizable products.
Water recycling isn’t just about meeting regulations – it’s a smart, forward-thinking strategy that lowers costs, protects resources, and strengthens the industry’s commitment to sustainable manufacturing.
FAQs
How does water recycling help lower production costs in bag manufacturing?
Water recycling plays a key role in cutting production costs for bag manufacturers. By reusing water during the production process, companies can reduce their reliance on purchasing fresh water and significantly lower the expenses tied to wastewater disposal. This creates a steady and cost-efficient water supply while streamlining operations.
Beyond the financial benefits, water recycling aligns with sustainable practices, which can boost a company’s image and meet growing consumer interest in environmentally friendly products. It’s a smart way to save money while taking steps toward a greener manufacturing process.
What challenges come with recycling wastewater during bag manufacturing?
Recycling wastewater in bag manufacturing comes with its fair share of hurdles. The process has to tackle a diverse mix of contaminants – plastics, dyes, adhesives, and cleaning chemicals – all of which can vary between production cycles. This inconsistency makes it tough to create a one-size-fits-all treatment solution. Manufacturers need systems capable of handling everything from solid particles, like polymer fragments, to dissolved substances, such as pigments and solvents. On top of that, cleaning operations generate significant amounts of sludge, adding another layer of complexity.
In the U.S., strict water reuse regulations further complicate the process. Manufacturers must carefully monitor and eliminate nutrients, heavy metals, and leftover chemicals to stay compliant. This often means turning to advanced technologies like reverse osmosis or membrane bioreactors. While effective, these solutions can drive up both costs and energy consumption. For companies like SACOS DE JUNYUAN, the key lies in investing in advanced filtration systems, precise monitoring tools, and smart water reuse strategies to cut expenses and minimize environmental impact.
How does using RPET materials make bag production more sustainable?
RPET, short for recycled polyethylene terephthalate, is created by transforming used plastic bottles into polyester fibers. This process helps reduce reliance on virgin petroleum-based materials, cutting down carbon emissions and conserving energy. Plus, it plays a crucial role in keeping millions of plastic bottles out of landfills and oceans, supporting a circular economy while tackling plastic waste.
When it comes to making bags, RPET delivers the same strength and quality as traditional polyester but uses less water and fewer chemicals during production. Companies like SACOS DE JUNYUAN incorporate RPET into their customizable bag designs, offering eco-friendly options that don’t compromise on performance. This method blends waste reduction, energy savings, and water conservation, positioning RPET as a standout choice for sustainable bag manufacturing.




 Telemóvel/What's App/Wechat
Telemóvel/What's App/Wechat E-Mail
E-Mail ADD
ADD




